Screen-printed p–n BiOCl/BiFeO3 heterojunctions for efficient photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B†
Abstract
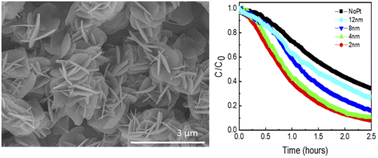
Colloidal-free screen-printed p–n BiOCl/BiFeO3 heterojunctions are successfully synthesized to achieve photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) using visible light (λ ≥ 400 nm). The crystalline structure of dense BiOCl nanosheets self-assembled with impressive aspect ratio atop BFO powders is confirmed by XRD, Raman and TEM measurements. Iron impurities inside these 10 ± 2 nm-thick BiOCl nanosheets increase visible light absorption. Fluorescent Rhodamine B (RhB) dye degradation is used to evaluate the photocatalytic performance of this unique heterojunction material. For optimal metal-enhanced RhB degradation, a few nanometers of platinum are deposited using the sputtering technique to act as a cocatalyst. This unique architecture yields an impressive 92% RhB degradation in only 150 min under visible light. Operating at near-neutral pH, the proposed approach also addresses the key issue of catalysis recovery, which remains one of the main drawbacks of current photocatalysis technologies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...