Preparation of a quartz microbalance sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymers and its application in formaldehyde detection
Abstract
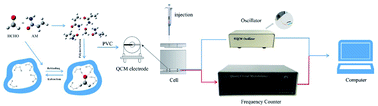
Quartz crystal microbalances (QCMs) have been widely used in the food industry, environmental monitoring, and biomedicine. Here, a molecularly imprinted QCM sensor was prepared and used for formaldehyde detection. Using polyvinyl chloride as the embedding material and tetrahydrofuran as the solvent, a QCM electrode was modified with HCHO molecularly imprinted polymers (HCHO-MIPs). The detection conditions of the sensor were optimized, and its selectivity was investigated. The theoretical calculation results revealed that the acrylamide and pentaerythritol triacrylate were potential candidate functional monomer and cross-linking agent, respectively, in the preparation of HCHO-MIPs with high adsorbability, superselectivity, and stability. According to the calculated results, a sensor had been prepared. When the pH was 7, the added mass of the HCHO-MIPs (or NIPs) was 20 mg, and the amount of PVC coating was 20 μL, the sensor exhibited good adsorption, selectivity, repeatability, high sensitivity, high accuracy, and a short response time. The lowest detection limit was 10.72 ng mL−1. The sensor exhibited higher selectivity for HCHO than for propionaldehyde and benzaldehyde. The HCHO contents in fresh shrimp samples were detected using the sensor for four cycles, and the detection rates were in the range of 97.56–98.60%. This study provided a theoretical and experimental basis for the rapid detection of HCHO.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...