High capacity all-solid-state lithium battery enabled by in situ formation of an ionic conduction path by lithiation of MgH2†
Abstract
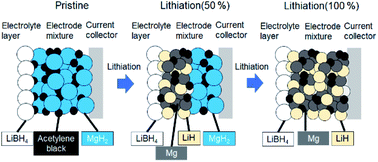
All-solid-state Li batteries have attracted significant attention because of their high energy density and high level of safety. In a solid-state Li-ion battery, the electrodes contain a solid electrolyte that does not contribute directly to the capacity. Therefore, a battery that does not require a solid electrolyte in its electrode mixture should exhibit a higher energy density. In this study, a MgH2 electrode was used as the negative electrode material without a solid electrolyte in its mixture. The resultant battery demonstrated excellent performance because of the formation of an ionic conduction path based on LiH in the electrode mixture. LiH and Mg clearly formed upon lithiation and returned to MgH2 upon delithiation as revealed by TEM-EELS analysis. This mechanism of in situ electrolyte formation enables the development of a solid-state battery with a high energy density.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...