Improved ORR/OER bifunctional catalytic performance of amorphous manganese oxides prepared by photochemical metal–organic deposition†
Abstract
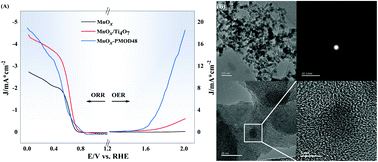
Transition metal oxide nanomaterials or nanocomposites containing transition metal oxides have the potential to replace traditional catalysts for electrochemical applications, photocatalysis, and energy storage. Amorphous manganese oxide catalysts were prepared via photochemical metal–organic deposition (PMOD). Through XRD, SEM-EDS, Raman spectroscopy, FTIR spectroscopy, HRTEM-EDS, and XPS, we confirmed that amorphous manganese oxide catalysts were successfully prepared. Amorphous catalysts prepared with different photolysis times were compared in terms of their performance for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER), and catalyst MnOx-PMOD48 showed the best performance because of its high Mn3+ proportion and electrochemically active surface area. MnOx-PMOD48 showed better ORR/OER performance than the crystalline MnOx and MnOx/Ti4O7 catalysts from our previous work. Following our previous work on crystalline manganese oxide catalysts, we added Ti4O7 during the PMOD process with 48 h of treatment and obtained the amorphous catalyst MnOx/Ti4O7-PMOD. MnOx/Ti4O7-PMOD was supported by Ti4O7 particles, which led to improved stability. The ORR/OER catalytic activity of MnOx/Ti4O7-PMOD was better than that of crystalline catalyst MnOx/Ti4O7-300, which was the best crystalline catalyst in our previous work. We also compared lithium-oxygen batteries assembled with MnOx/Ti4O7-PMOD and MnOx/Ti4O7-300. The battery performance tests confirmed that the amorphous manganese catalyst had better ORR/OER bifunctional catalytic performance than the crystalline manganese catalyst because of its high defect state with more abundant edge active sites and more surface-exposed catalytic active sites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...