Solar-driven aromatic aldehydes: green production from mandelic acid derivatives by a Co(ii)/C3N4 combined catalyst in aqueous media†
Abstract
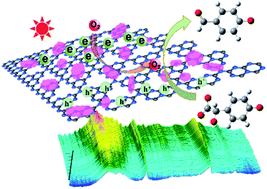
According to the requirements for sustainable development, reclaiming fine chemicals from wastewater under mild conditions is an extremely significant line of research. A low-cost and high-efficiency polydentate chelate- and polymeric Co(II)-based complex (Co-L)-loaded C3N4 photocatalyst (Co-L/C3N4) was constructed and used to convert aromatic mandelic acids in wastewater at room temperature. The BET specific surface area increased from 28 m2 g−1 to 68 m2 g−1, indicating its excellent absorptive character. The light absorption range of Co-L/C3N4 reached 650 nm, while the band energy reduced to 2.30 eV, which caused a significant enhancement in photocatalytic activity. The conversion of substituted mandelic acids was more than 90% due to the photoactivity of Co-L/C3N4. Time-resolved PL spectra indicated the remarkable separation of the photogenerated electron–hole pairs in Co-L/C3N4. Furthermore, the UV-vis and in situ FTIR spectra indicated the formation of aldehyde groups in the selective oxidation process, which provided support for the plausible catalytic mechanism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...