Dual-responsive degradable core–shell nanogels with tuneable aggregation behaviour†
Abstract
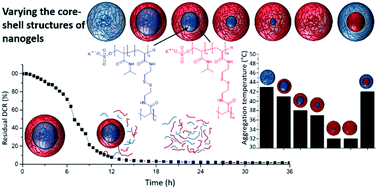
We report the synthesis of core–shell nanogels by sequential addition of thermoresponsive monomers; N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) and N-isopropylmethacrylamide (NIPMAM). The aggregation behaviour of aqueous dispersions of these particles in the presence of salt can be tuned by varying the monomer ratio. The inclusion of degradable cross-linker bis(acryloyl)cystamine (BAC) allows the nanogels to degrade in the presence of reducing agent, with nanogels composed of a copolymer of the two monomers not showing the same high levels of degradation as the comparable core–shell particles. These levels of degradation were also seen with physiologically relevant reducing agent concentration at pH 7. Therefore, it is hoped that the aggregation of these nanogels will have applications in nanomedicine and beyond.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...