A thermo-, near-infrared light- and water-induced shape memory polymer with healing fatigued shape memory performance†
Abstract
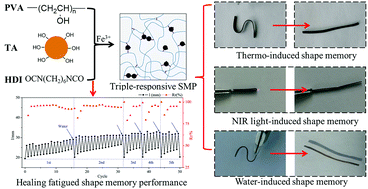
Although multi-responsive shape memory polymers (SMPs) have been rapidly developed in recent years due to their wide application in sensors, actuators and biomedical devices, their fabrication via a facile approach is still a challenge. Herein, a shape memory polymer with excellent thermo-, near-infrared (NIR) light- and water-induced shape memory performance was fabricated by introducing tannic acid/ferric ion (TA/Fe3+) coordination into cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA). The shape memory performance was achieved by cross-linking PVA and TA with hexamethylene diisocyanate, while the NIR light and water responsiveness were provided by the photothermal effects of TA/Fe3+ and the hydrophilic nature of PVA, respectively. The shape recovery ratio induced by all three stimuli could reach over 95%. Moreover, it was found that the fatigued shape memory performance can be healed by simply immersing materials into water, and it was also applicable for other thermoset SMPs using suitable solvents, which could greatly improve the service life and reliability of SMPs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...