Structural investigation of the efficient capture of Cs+ and Sr2+ by a microporous Cd–Sn–Se ion exchanger constructed from mono-lacunary supertetrahedral clusters†
Abstract
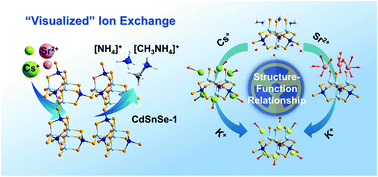
Visualization of the ion exchange mechanism for 137Cs and 90Sr decontamination is important for safe radioactive liquid waste reprocessing and emergency response improvement in the event of a nuclear accident. Here, the remediation of Cs+ and Sr2+ was achieved through ion exchange using a cadmium selenidostannate, [CH3NH3]3[NH4]3Cd4Sn3Se13·3H2O (CdSnSe-1), with rapid exchange kinetics, high β/γ radiation resistances, broad pH durability and facile elution. The framework constructed from mono-lacunary supertetrahedral clusters features a great negative charge density of 3.27 × 10−3 that accounts for the superhigh exchange capacities of 371.4 (Cs+) and 128.4 mg g−1 (Sr2+). Single-crystal structural analysis on the exchanger during the “pristine–ion exchange–elution” cycle supplies instructive information to elucidate the uptake and recycle mechanism for Cs+ and Sr2+. The broken symmetry of the cluster caused by a vacant site, combined with the co-templating effects of mixed methylammonium/ammonium, contributes to the formation of voids I and II that show adsorption activity for both Cs+ and K+ ions. In comparison, the divalent Sr2+ ions with higher hydration degree exchange with (alkyl)ammonium cations in a 1 : 2 molar ratio, resulting in its location at a new void (III) closer to the framework and thus a higher binding strength. The energy variation during the adsorption process based on a DFT calculation illustrates the high efficiency of CdSnSe-1 for capture of both Cs+ and Sr2+. This “visualized” ion exchange underlines the robustness and flexibility of CdSnSe-1 as a Cs+ and Sr2+ trapper, and reveals the deeper structure–function relationship from a new surface interaction viewpoint.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...