A degradable, broad-spectrum and resistance-resistant antimicrobial oligoguanidine as a disinfecting and therapeutic agent in aquaculture†
Abstract
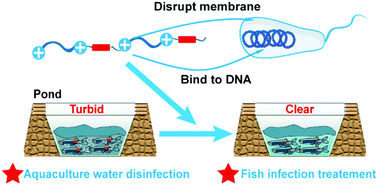
The threat of antibiotic resistance to community healthcare and the global economy has raised extensive concern, and the over-use of antibiotics in animal husbandry plays a significant role in the occurrence and spread of resistance genes. An emerging solution for the above problem is the development of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) and their mimics as alternative disinfectants in agriculture and aquaculture. These antibacterial agents usually exhibit excellent potency and a low drug resistance generation rate, but are highly cytotoxic to eukaryotes and thus post safety concerns. Here, we report our solution to this problem by introducing degradable linkers in oligoguanidine-based antimicrobial peptidomimetics with a dual-selective mechanism of action. With both bacterial membrane and DNA targeting capability, the hit peptidomimetic exhibited higher therapeutic indices and synergistic effects with other antibiotics, while its fast antimicrobial kinetics and low resistance rate were maintained. In addition, the added degradable feature improved the biocompatibility and environmental sustainability of this material. The oligoguanidine-based hit peptidomimetic also showed good activity in vivo, as it did not cause observable toxicity in zebrafish, and it could significantly improve the survival rate of zebrafish in a scratch wound infection model.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...