Microfluidic-supported synthesis of anisotropic polyvinyl methacrylate nanoparticles via interfacial agents†
Abstract
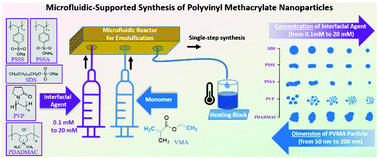
For polymer particles, recent studies emphasized that the particle shape—not size—plays the dominant role in novel applications in fields ranging from nanotechnology, biomedicine, to photonics, which has intensified the quest for fabrication platforms of polymer colloids with complex non-spherical (anisotropic) shapes. Here, we developed a single-step, microfluidic-supported synthesis for anisotropic polyvinyl methacrylate (PVMA) nanoparticles (NPs) by combining the advantages of microfluidics (providing homogeneous conditions for the initial emulsification process) and bulk batch synthesis (providing inhomogenous conditions for the thermal polymerization). Specifically, we tested five interfacial agents regarding their direct impact on the NP shape (from isotropic spherical to anisotropic flower-like shapes) and their concentration-dependent impact (from 0.1 mM to 20 mM) on the NP diameter (from 200 nm to 50 nm). We employed vinyl methacrylate (VMA), a monomer offering two-polymerization active sites. With our work, we contribute to a fundamental understanding of colloidal polymerization towards predictive shapes below the critical 200 nm regime.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...