C-Methylation controls the biosynthetic programming of alternapyrone†
Abstract
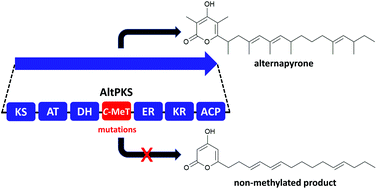
Alternapyrone is a highly methylated polyene α-pyrone biosynthesised by a highly reducing polyketide synthase. Mutations of the catalytic dyad residues, H1578A/Q and E1604A, of the C-methyltransferase domain resulted in either significantly reduced or no production of alternapyrone, indicating the importance of C-methylation for alternapyrone biosynthesis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...