Structure-activity relationship and bioactivity studies of neurotrophic trans-banglene†
Abstract
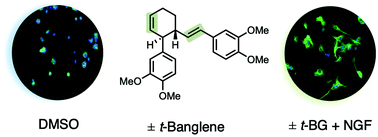
The synthesis and bioactivity of neurotrophic banglenes and derivatives is described, establishing a structure–activity relationship which enables future mechanistic studies. Neuritogenesis assays indicate that (−) trans-banglene is the active enantiomer. Assays performed with and without NGF protein suggest that neurotrophic activity and potentiation of NGF activity by (−) trans-banglene might be distinct unassociated processes. Interestingly, (−) trans-banglene potentiation of NGF-induced neuritogenesis is unaffected by the presence of Erk1/2, Akt and Pkc inhibitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...