Recent developments in enantio- and diastereoselective hydrogenation of N-heteroaromatic compounds
Abstract
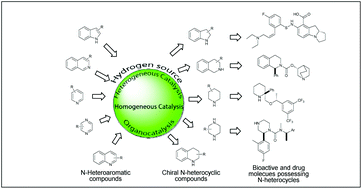
The enantioselective and diastereoselective hydrogenation of N-heteroaromatic compounds is an efficient strategy to access chirally enriched cyclic heterocycles, which often possess highly bio-active properties. This strategy, however, has only been established in recent times. This is in part due to the challenges of the high stability of the aromatic compounds and the presence of heteroatoms that have the potential to poison the chiral catalysts. Additionally, N-heteroaromatic compounds are a structurally diverse family of substrates, each group showing distinct reactivity in hydrogenation. Advances in recent years have allowed various N-heteroaromatic compounds, including pyridines, indoles, quinolines, isoquinolines, quinoxalines and imidazoles, to be hydrogenated with good to excellent enantioselectivity under appropriate reaction conditions. Transition–metal catalysis, utilising iridium, ruthenium, rhodium, and palladium complexes, has been found to play an important role in this field. More recently, organocatalysis has been shown to be efficient for the hydrogenation of certain N-heteroaromatic compounds. This review provides an analysis of the recent developments in the enantioselective and diastereoselective hydrogenation of N-heteroaromatic compounds. The importance of these molecules and their applications to drug discovery has been highlighted throughout the review.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Synthetic methodology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...