Novel electrospun chitosan/PEO membranes for more predictive nanoparticle transport studies at biological barriers†
Abstract
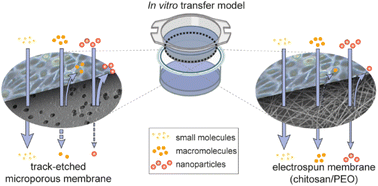
The design of safe and effective nanoparticles (NPs) for commercial and medical applications requires a profound understanding of NP translocation and effects at biological barriers. To gain mechanistic insights, physiologically relevant and accurate human in vitro biobarrier models are indispensable. However, current transfer models largely rely on artificial porous polymer membranes for the cultivation of cells, which do not provide a close mimic of the natural basal membrane and intrinsically provide limited permeability for NPs. In this study, electrospinning is exploited to develop thin chitosan/polyethylene oxide (PEO) membranes with a high porosity and nanofibrous morphology for more predictive NP transfer studies. The nanofiber membranes allow the cultivation of a tight and functional placental monolayer (BeWo trophoblasts). Translocation studies with differently sized molecules and NPs (Na-fluorescein; 40 kDa FITC-Dextran; 25 nm PMMA; 70, 180 and 520 nm polystyrene NPs) across empty and cell containing membranes reveal a considerably enhanced permeability compared to commercial microporous membranes. Importantly, the transfer data of NPs is highly similar to data from ex vivo perfusion studies of intact human placental tissue. Therefore, the newly developed membranes may decisively contribute to establish physiologically relevant in vitro biobarrier transfer models with superior permeability for a wide range of molecules and particles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...