In vivo delivery of nuclear targeted drugs for lung cancer using novel synthesis and functionalization of iron oxide nanocrystals†
Abstract
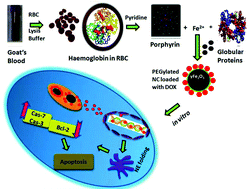
Iron nanoparticles are typically made from inorganic precursors, but for the first time, we synthesized-Fe2O3-NCs from goat blood (a bio-precursor) employing the RBC lysis method (a molecular level approach). After that, γ-Fe2O3-NPs were coated with PEG and combined with DOX to form nanocarriers (NC) for drug delivery. PEG–DOX–γ-Fe2O3-NCs were physicochemically investigated using A549 lung cancer cells as a model for in vitro and in vivo studies. The result revealed that PEG–DOX–γ-Fe2O3-NCs were 60–70 nm in size, confirming the presence of PEG and DOX in γ-Fe2O3-NCs. Cytotoxicity, morphological abnormalities, and intracellular iron recognition were observed in a dose-dependent manner in the cell line investigation. The presence of robust DOX signals in the nucleus shows that PEG–DOX–γ-Fe2O3-NCs were used for nuclear chemotherapy and cell uptake. In vivo, the rapid release of PEG–DOX–γ-Fe2O3-NCs was also observed. DOX suppresses carcinogenesis and has no toxicity in the healthy organs of tumor-bearing mice, according to investigated histological study. As a result, PEG–DOX–γ-Fe2O3-NCs synthesized from natural sources will be preferable to commercially available synthetic sources and can be employed as an anticancer agent. This nanocarrier will be developed in the future with various drug carrier systems for targeted nuclear treatment of cancer and other related diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...