Iridoid glycoside isolated from Wendlandia glabrata and the role of its enriched fraction in regulating AMPK/PEPCK/G6Pase signaling pathway of hepatic gluconeogenesis†
Abstract
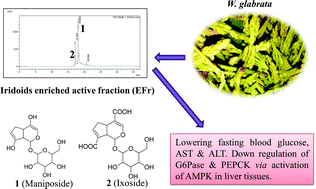
The present study aims for phytochemical investigation and mechanistic analysis of the antihyperglycemic effect of Wendlandia glabrata DC, a lesser explored traditional herb used by the indigenous communities of North East India for obesity, diabetes, and related metabolic syndrome. The phytochemical study resulted in the isolation of eight compounds, including a novel iridoid glycoside (1), another iridoid (2), condensed tannins (3,4), and flavonoids (5–8). Iridoid glycosides, because of their easy absorption, versatile modifiability, and prominent bioactivity against various diseases, have shown importance in the phytopharmaceutical research area. The novel iridoid enriched fraction (EFr) from W. glabrata showed significant blood glucose lowering potential to near normal (96.25 ± 11.17 mg dl−1) in STZ-induced diabetic Swiss albino mice (>230 mg dl−1). Additionally, an immunoblotting investigation showed that EFr prevented hepatic gluconeogenesis conditions with a significant increase in AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation up to 1.4–1.7 folds and downregulated key gluconeogenic enzymes glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK). Moreover, the major active novel compound 1 exhibited significant glucose uptake at 6 μM concentration in vitro in free fatty acid (FFA) induced CC1 hepatocytes. Taken together, these findings demonstrated that enriched fraction (EFr) of W. glabrata ameliorated hepatic insulin resistance in diabetes via regulating AMPK/PEPCK/G6Pase signaling pathway of hepatic glucose metabolism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...