A switchable electrochemical hairpin-aptasensor for ochratoxin A detection based on the double signal amplification effect of gold nanospheres
Abstract
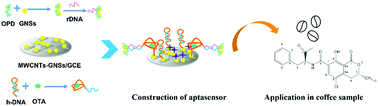
Ochratoxin A (OTA) is a ubiquitous food contaminant and can cause serious harm to human health. Herein, a switchable electrochemical hairpin-aptasensor for OTA detection was established. Hairpin-DNA (h-DNA) was designed as a signal switch consisting of an anti-OTA aptamer (OTA-apt) and complementary DNA (cDNA). Gold nanospheres (GNSs) were combined with multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) to establish a great support interface (MWCNTs/GNSs). Meanwhile, conjugated polymer–nanoparticle composites (POPD-GNSs) were prepared and utilized to label report DNA (rDNA), forming a signal probe (POPD-GNSs-rDNA). In the presence of OTA, a configuration change was triggered and switched on the h-DNA, leading to the exposure of cDNA, which is complementary with the rDNA. Therefore, POPD-GNSs-rDNA was introduced on the electrode and produced strong electrical signals (signal on). GNSs played the role of double signal amplification in the switchable electrochemical hairpin-aptasensor. Thus, a low limit of detection of 1 pg mL−1 was obtained and the monitoring range was from 2 pg mL−1 to 1 ng mL−1. Moreover, the practicability and reliability of the constructed aptasensor was verified by detecting OTA in coffee samples. The satisfactory recovery demonstrates the potential application of this aptasensor in OTA monitoring for food security. This strategy is also applicable to the detection of other small molecule contaminants in food.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...