Rbm20 ablation is associated with changes in the expression of titin-interacting and metabolic proteins†
Abstract
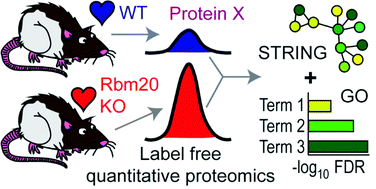
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a major risk factor for developing heart failure and is often associated with an increased risk for life-threatening arrhythmia. Although numerous causal genes for DCM have been identified, RNA binding motif protein 20 (Rbm20) remains one of the few splicing factors that, when mutated or genetically ablated, leads to the development of DCM. In this study we sought to identify changes in the cardiac proteome in Rbm20 knockout (KO) rat hearts using global quantitative proteomics to gain insight into the molecular mechanisms precipitating the development of DCM in these rats. Our analysis identified changes in titin-interacting proteins involved in mechanical stretch-based signaling, as well as mitochondrial enzymes, which suggests that activation of pathological hypertrophy and altered mitochondrial metabolism and/or dysfunction, among other changes, contribute to the development of DCM in Rbm20 KO rats. Collectively, our findings provide the first report on changes in the cardiac proteome associated with genetic ablation of Rbm20.
- This article is part of the themed collection: US HUPO – Proteomics from Single Cell to Systems Biology in Health and Disease


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...