Stereoisomeric Pam2CS based TLR2 agonists: synthesis, structural modelling and activity as vaccine adjuvants†
Abstract
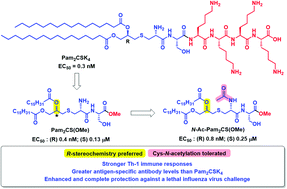
Lipopeptides including diacylated Pam2CSK4 as well as triacylated Pam3CSK4 act as ligands of toll-like receptor (TLR)-2, a promising target for the development of vaccine adjuvants. The highly investigated Pam2CSK4 and Pam3CSK4, despite their aqueous solubility have not performed well as vaccine adjuvants which may be attributable to potential denaturation of protein antigens by these cationic surfactant-like lipopeptides. In the present investigation, we synthesized (R), (S) and racemic Pam2CS(OMe) analogs and their N-acetyl derivatives without the tetralysine component to systematically investigate the effect of stereochemistry at the thio-glycerol lipopeptide core of these lipopeptide based TLR2 agonists. The resulting compounds were compared using TLR2 reporter cell-based assays and the ability of the synthesized lipopeptides to stimulate cytokine production (IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α) by freshly collected human PBMCs and CD40 and CD86 expressions by mouse spleen cells was also investigated. Notably, few synthesized lipopeptides were found to be potent TLR2/6 agonists, inducing cytokine production and upregulating CD40 and CD86 expressions. The TLR2/6 agonistic lipopeptides were further assessed for vaccine adjuvant effects in mice. The results confirmed that the R-stereochemistry at the thio-glycerol lipopeptide core was preferred for maximal TLR2/6 activity, as reflected in Th1 immune deviation, higher antibody levels and enhanced vaccine protection against a lethal influenza challenge.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...