Armeniaspirol analogues with more potent Gram-positive antibiotic activity show enhanced inhibition of the ATP-dependent proteases ClpXP and ClpYQ†
Abstract
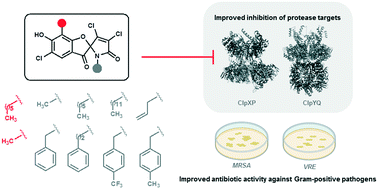
Antibiotics with fundamentally new mechanisms of action such as the armeniaspirols, which target the ATP-dependent proteases ClpXP and ClpYQ, must be developed to combat antimicrobial resistance. While the mechanism of action of armeniaspirol against Gram-positive bacteria is understood, little is known about the structure–activity relationship for its antibiotic activity. Based on the preliminary data showing that modifications of armeniaspirol's N-methyl group increased antibiotic potency, we probed the structure–activity relationship of N-alkyl armeniaspirol derivatives. A series of focused derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for antibiotic activity against clinically relevant pathogens including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus. Replacement of the N-methyl with N-hexyl, various N-benzyl, and N-phenethyl substituents led to substantial increases in antibiotic activity and potency for inhibition of both ClpYQ and ClpXP. Docking studies identified binding models for ClpXP and ClpYQ that were consistent with the inhibition data. This work confirms the role of ClpXP and ClpYQ in the mechanism of action of armeniaspirol and provides important lead compounds for further antibiotic development.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...