A MnOx–graphitic carbon composite from CO2 for sustainable Li-ion battery anodes†
Abstract
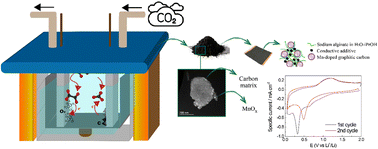
The increasing concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere is the leading cause of the greenhouse gas effect. Carbon capture and storage is an important topic to develop sustainable technologies. Molten salt CO2 capture and electrochemical transformation represent a suitable process to produce various carbon products, such as carbon nanofibers, carbon nanotubes, graphite, and graphene. The employment of graphitic anode materials for Li-ion batteries coming from CO2 capture is ideal for increasing battery sustainability. Moreover, the addition of transition metal oxides represents a suitable strategy for new negative electrodes because conversion reactions lead to high specific capacities. Among them, manganese has gained attention due to its multiple valence states and numerous possible crystalline structures. In the present work, a MnOx–graphitic carbon composite obtained by electrolysis of CO2via molten Li2CO3 is characterized and used to prepare a negative electrode for LIBs with an environmentally sustainable aqueous process.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Energy Frontiers: Electrochemistry and Electrochemical Engineering, Celebrating materials science in Italy and Popular Advances


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...