A microfluidic-informatics assay for quantitative physical occlusion measurement in sickle cell disease†
Abstract
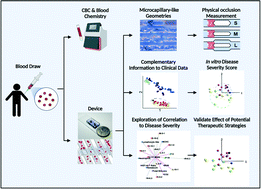
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a genetic condition that causes abnormalities in hemoglobin mechanics. Those affected are at high risk of vaso-occlusive crisis (VOC), which can induce life-threatening symptoms. The development of measurements related to vaso-occlusion facilitates the diagnosis of the patient's disease state. To complement existing readouts, we design a microfluidic-informatics analytical system with varied confined geometries for the quantification of sickle cell disease occlusion. We detect an increase in physical occlusion events in the most severe hemoglobin SS group. We use bioinformatics and modeling to quantify the in vitro disease severity score (DSS) of individual patients. We also show the potential effect of hydration, clinically recommended for crisis management, on reducing the disease severity of high-risk patients. Overall, we demonstrate the device as an easy-to-use assay for quick occlusion information extraction with a simple setup and minimal additional instruments. We show the device can provide physical readouts distinct from clinical data. We also show the device sensitivity in separate samples from patients with different disease severity. Finally, we demonstrate the system as a potential platform for testing the effectiveness of therapeutic strategies (e.g. hydration) on reducing sickle cell disease severity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...