Development of an ammonia pretreatment that creates synergies between biorefineries and advanced biomass logistics models†
Abstract
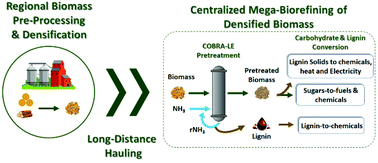
A novel ammonia-based pretreatment for densified lignocellulosic biomass was developed to reduce ammonia usage and integrate with viable biomass logistics scenarios. The COmpacted Biomass with Recycled Ammonia (COBRA) pretreatment performed at 100 °C allows >95% conversion of sugarcane bagasse (SCB) carbohydrates into soluble monomeric and oligomeric sugars (glucose and xylose) using industrially relevant 6% glucan loading (∼21% solids loading) enzymatic hydrolysis conditions at reduced enzyme loadings. Pretreatment via COBRA with simultaneous lignin extraction (COBRA-LE) improved Saccharomyces cerevisiae 424A(LNH-ST) metabolic yield from 89% to 97.5% relative to COBRA without delignification, allowing a process ethanol yield of 71.6%. A technoeconomic analysis on SCB biorefining to ethanol in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, compared COBRA to other mature technologies, such as AFEX and steam-explosion. Amongst all scenarios studied, biorefineries based on COBRA-LE pretreatment offered the lowest average minimum ethanol selling price of US$1.45 per gallon ethanol. COBRA pretreatment was subsequently tested on perennial grasses and hardwoods, and >80% total sugar yields were achieved for all cases.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2022 Green Chemistry Hot Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...