Towards highly efficient continuous-flow catalytic carbon dioxide cycloadditions with additively manufactured reactors†
Abstract
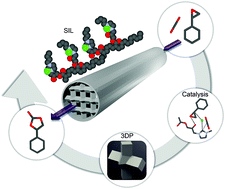
Developing efficient and sustainable methodologies to transform CO2 into added-value chemicals is an important strategy for decarbonization in the chemical industry. Here, a new multi-scale approach for the cycloaddition of CO2 to epoxides is reported, designed by combining the hydrogen bonding ability, metal-free catalysts and supported ionic liquids on polymers. The use of additive manufacturing (AM) techniques allowed the digital design and rapid fabrication of structured architectures for continuous-flow reactors, which offers potential for process optimization. AM generated catalytic reactors showed higher catalytic activity than similar sized packed bed reactors, when normalised to the amount of catalyst and their surface area. The catalytic activity and stability were maintained over a prolonged period of time (300 h) without loss of activity, and it was demonstrated to efficiently transform a range of epoxide substrates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...