Release of an anti-anxiety peptide in casein hydrolysate with Aspergillus oryzae protease†
Abstract
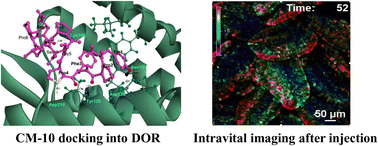
Food protein-derived peptides with agonistic effects on receptors have great potential for treating anxiety, hypertension, and stress. In the present study, opioid peptides with agonistic activities for δ-receptor-expressing HEK293 cells were screened from casein hydrolysates prepared with five types of food grade proteolytic enzymes, among which casein hydrolysate with Aspergillus oryzae protease ASD showed the highest opioid activity. Eluted fractions showing potent opioid activity were further purified for active peptides by reverse phase-HPLC. The peptide in the active fraction was identified as YPFPGPIPNS, a member of β-casomorphin (CM-10) (β-casein 60–69). Various CM-10 derivative peptides were synthesized and their characteristic features for specificities towards δ- and μ-receptors were determined. Peptides 5 to 12 amino acids long showed relatively higher opioid activities for δ- and μ-receptors. CM-10 was docked into the optimized δ-receptor model. The CDOCKER energies of the CM-10 derivatives were consistent with their opioid activities. In the elevated plus-maze study, CM-10 showed a significant anti-anxiety effect in BALB/c mice at a dose of 10 mg per kg body weight when administered orally, but not via intravenous injection. Furthermore, intravital imaging revealed that Ca2+ signaling was induced in the small intestinal villi of a Yellow Cameleon 3.60 (YC3.60)-expressing mouse upon injection with CM-10. However, this decreased in the presence of δ- or μ-receptor antagonists. These results suggest that the opioid peptide CM-10 prepared from casein with ASD has an anti-anxiety effect through interaction with gut δ- and/or μ-opioid receptors in the mouse gut.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...