Effects of marginal zinc deficiency on learning and memory ability after birth†
Abstract
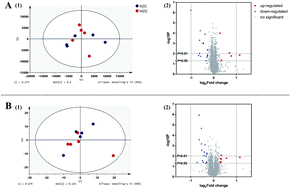
Zinc deficiency during pregnancy and severe zinc deficiency after birth both impaired learning and memory ability, but the effects of marginal zinc deficiency (MZD) after birth on learning and memory are unclear. In the first experiment, 4-week-old male rats were randomly divided into three groups: the marginal zinc-deficient group (MZG, 10 mg kg−1, 1/3 RNI), normal zinc group (NZG, 30 mg kg−1, RNI), and paired zinc group (PZG, 30 mg kg−1). After a 4-week feeding period, the brain weight, brain coefficient, and serum zinc concentration were measured, and hippocampal proteomics analysis was performed. In the second experiment, 4-week-old male rats were fed the same diet for 8 weeks. In addition to the previously mentioned indicators, the Morris water maze results, brain pathology, post-translational modifications (PTMs) of hippocampal proteins, and the concentrations of indicators known to be related to learning and memory were analyzed. In both experiments, compared with those of the NZG, the food intake, body weight and serum zinc of the MZG were significantly decreased, and the brain weight was unchanged, but the brain coefficient was increased. Two hippocampal proteomics analyses and PTM screening showed that MZD did not change the expression and PTM of proteins. The brain pathology, learning, memory and the concentrations of indicators known to be related to learning and memory were not changed by MZD. Our study confirmed that marginal zinc deficiency (10 mg kg−1, 1/3 RNI) had no effect on the learning and memory abilities of rats after birth.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...