A comparative study between olive oil and corn oil on oxidative metabolism
Abstract
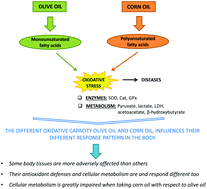
Fats are an important part of diet, but not all lipids have the same structure and chemical properties. Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds in their structure and can be monounsaturated or polyunsaturated, respectively. Most vegetable oils, such as olive oil and corn oil, contain significant amounts of these fatty acids. The presence of double bonds in the molecule of a fatty acid constitutes vulnerable sites for oxidation reactions generating lipid peroxides, potentially toxic compounds that can cause cellular damage. In response to this oxidative damage, aerobic organisms have intracellular enzymatic antioxidant defense mechanisms. The aim of the present investigation was to study comparatively the effects of control liquid diets, of a defined composition, containing olive oil or corn oil as a lipid source respectively of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids, on the oxidative metabolism of rats. Rats were divided into three groups which received a control animal feed diet (A.F.), olive oil liquid diet (O.O) and corn oil liquid diet (C.O) for 30 days. It was observed that the activity of the antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), increased in the liver and white fat tissue of rats fed with olive oil when compared to the corn oil group. However, in brown fat tissue and blood cells, the enzyme activities showed a tendency to decrease in the olive oil group. In addition, the effect of olive oil and corn oil on several glucose metabolism parameters (pyruvate, lactate, LDH, acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate) showed that corn oil impairs to a greater extent the cellular metabolism. All these results helped in concluding that some body tissues are more adversely affected than others by the administration of corn oil or olive oil, and their antioxidant defenses and cellular metabolism respond differently too.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...