Rosmarinic acid ameliorated psoriatic skin inflammation in mice through the novel inhibition of the interleukin-17A/interleukin-17A receptor interaction
Abstract
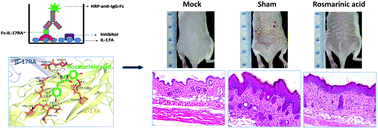
The interaction between interleukin-17A (IL-17A) and IL-17A receptor (IL-17RA) is a crucial target of psoriasis. Several natural compounds from foods or herbs have displayed efficacies on the amelioration of psoriasis. However, the anti-psoriatic mechanisms are mostly through the common anti-inflammatory effects and rarely via the blockage of the IL-17A/IL-17RA interaction. In this study, the IL-17A/IL-17RA-targeting effects of phenylpropanoids, a large class of secondary metabolites in plants, were analyzed. By screening 17 phenylpropanoids, we found that top four compounds with IL-17A/IL-17RA-blocking abilities were rosmarinic acid, eugenol, syringic acid, and gallic acid, with inhibitory concentrations at 50% of 2.14 ± 0.35 mM, 6.35 ± 0.1 mM, 4.79 ± 0.2 mM, and >10 mM, respectively. The oral administration of rosmarinic acid ameliorated redness and scaling on the dorsal skin of imiquimod-induced psoriatic mice in a dose-dependent manner. Rosmarinic acid suppressed the production of IL-23 and IL-17A and the infiltration of granulocyte subsets in skin tissues. Docking analysis showed that rosmarinic acid docked into IL-17A/IL-17RA interaction regions and exhibited hydrogen bonding with Arg-61, Glu-68, Arg-100, and Ser-118 of IL-17A, which are located in the epitope regions recognized by IL-17A neutralizing antibodies Fab6785 and Fab6468. In conclusion, this is the first study reporting that rosmarinic acid is an IL-17A-targeting agent that ameliorates psoriatic skin inflammation in mice via blocking the IL-17A/IL-17RA interaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...