Multi-omics reveals host metabolism associated with the gut microbiota composition in mice with dietary ε-polylysine†
Abstract
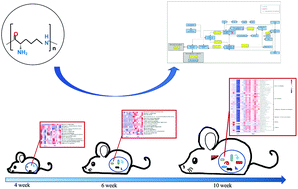
This study aimed to assess the influence of dietary supplementation of ε-polylysine on the gut microbiota and host nutrient metabolism, which is not systematically discussed by multi-omics analysis. A total of 40 mice were randomly divided into two groups exposed to either a basal diet (AIN-76A) or a basal diet with 150 ppm ε-polylysine. Fecal samples were collected for gut bacteria identification. Liver and plasma samples were collected for metabolomic and proteomic analyses. The results showed that ε-polylysine decreased the body weight of mice and affected the presence of certain types of intestinal microorganisms. The richness of the microbiota and number of phyla increased with age. ε-Polylysine affected the presence of genera and species, and either regulated or took part in the metabolism of energy, nitrogen, amino acids, lipids, carbohydrates, glycans, cofactors, and vitamins. The metabolite profiling showed that lipid and lipid-like molecules metabolites occupied the majority percent of plasma and liver metabolites. Additionally, ε-polylysine regulated the key role of metabolites and related metabolic enzymes in the metabolic pathways, especially phospholipid metabolism. In conclusion, dietary ε-polylysine improved the immunity of growing mice, and had a greater effect on the anabolism of nutrients in adult mice.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...