Resveratrol alleviates enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88-induced damage by regulating SIRT-1 signaling in intestinal porcine epithelial cells
Abstract
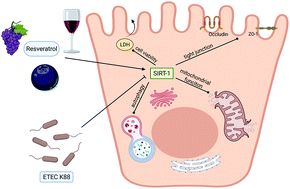
This study found that resveratrol pretreatment attenuated porcine intestinal epithelial cell damage caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) K88 in vitro and the protective effects of resveratrol were associated with SIRT-1 signaling. ETEC K88 is a main intestinal pathogen for post-weaning diarrhea (PWD) in piglets. With the strict ban on antibiotics in animal feed, people are seeking effective antibiotic substitutes to protect the intestinal system against harmful pathogenic bacteria. This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of resveratrol, a natural plant polyphenol, on ETEC K88-induced cellular damage in porcine enterocytes and underlying mechanisms. Intestinal porcine epithelial cell line 1 (IPEC-1) cells, pretreated with or without resveratrol (30 μM, 4 h), were challenged with ETEC K88 (MOI = 1 : 10) for 3 h. The results showed that ETEC K88 infection induced severe damage and dysfunction in IPEC-1 cells, as evidenced by a reduced cell viability, decreased tight junctions, mitochondrial dysfunction, and autophagy. It is noteworthy that IPEC-1 cells pre-treated with resveratrol improved their capacity for resistance to most of these abnormal phenotypes caused by ETEC K88 infection. Furthermore, we found that the activation of SIRT-1 signaling was associated with the benefits of resveratrol, as demonstrated by EX-527, an inhibitor of SIRT-1, which reversed most of the protective effects of resveratrol. In conclusion, these results indicated that resveratrol could protect intestinal epithelial cells against ETEC K88 infection by activating SIRT-1 signaling. These findings provide new insights into the role of resveratrol in maintaining intestinal physiological functions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...