Effect of combined treatment of l-arginine and transglutaminase on the gelation behavior of freeze-damaged myofibrillar protein
Abstract
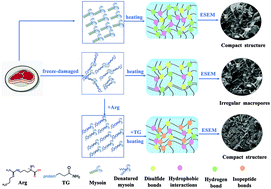
This research focused on the effects of L-arginine (Arg, 5 mM), transglutaminase (TG, E : S = 1 : 500), and the combination (Arg + TG) on the physicochemical properties and heat-induced gel performance of freeze-damaged myofibrillar protein (MP). The incorporation of Arg decreased the α-helix percentage (48.4%) and the mean particle size of freeze-damaged MP, as well as cooking loss (46.5%) and the overall textural characteristics of MP gels. The addition of TG reduced the α-helix content by 10.7% but significantly enhanced the crosslinking and heat-induced gel behavior of freeze-damaged MP, resulting in a slight reduction of cooking loss (17.7%) and the most ideal textural properties of MP gels. Although the presence of Arg remarkably suppressed the heat-induced development of storage modulus (G′) and reduced the hardness of MP gels (by 13.4%), the combination (Arg + TG) showed the lower cooking loss and the improved textural characteristics, with the set gel displaying the most delicate and compact microstructure. These findings indicated that the combination of Arg and TG could be a potential strategy to enhance the gelling performance of freeze-damaged meat proteins.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...