Total flavonoids in Epimedium koreanum Nakai alleviated chronic renal failure via promoting AMPK activation†
Abstract
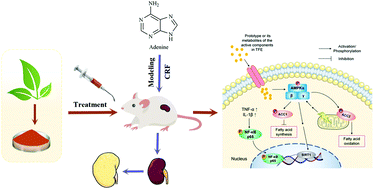
Chronic renal failure (CRF) is a result of the progression of chronic kidney diseases (CKD), a global health problem with a high cost of treatment and no ideal therapy. The aim of this study is to evaluate the pharmacological efficacy of the total flavonoids in Epimedium koreanum Nakai (TFE), a dietary supplement, against CRF and to determine the mechanism of actions. An adenine-induced CRF rat model and a TGF-β1 induced human kidney proximal tubule epithelial (HK-2) cell based in vitro renal fibrosis model were established and used to evaluate TFE's efficacy. Renal hemodynamics, biochemical indexes, inflammatory cytokines, histopathology and the reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels were determined to evaluate the efficacy of TFE on CRF. NMR-based metabolomics, immunohistochemical (IHC) staining, immunofluorescence (IF) staining, quantitative real time-PCR (qRT-PCR) and western blotting were conducted to determine the mechanism. The results showed that TFE had a significant effect on CRF at 150 mg kg−1 d−1 and could significantly alleviate renal fibrosis in the animal model. Twelve potential biomarkers, which mainly involve energy metabolism pathways, for CRF were identified using the metabolomics approach. The mechanism study suggested that TFE regulated AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and AMPK/silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1)/nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) signaling pathways. Furthermore, the effect of TFE was inhibited by compound C in the in vitro experiment, which also confirmed the above conclusion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...