l-Methionine supplementation attenuates high-fat fructose diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by modulating lipid metabolism, fibrosis, and inflammation in rats†
Abstract
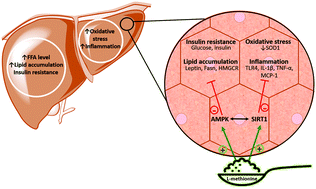
Recently, the protective effects of a methionine-rich diet on hepatic oxidative stress and fibrosis have been suggested but not adequately studied. We, therefore, hypothesized that L-methionine supplementation would ameliorate the progression of hepatic injury in a diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) model and aimed to investigate the underlying mechanism. NASH was developed in male Sprague Dawley rats by feeding them with a high-fat-fructose diet (HFFrD) for 10 weeks. The results demonstrated that L-methionine supplementation to NASH rats for 16 weeks improved the glycemic, lipid, and liver function profiles in NASH rats. Histological analysis of liver tissue revealed a remarkable improvement in the three classical lesions of NASH: steatosis, inflammation, and ballooning. Besides, L-methionine supplementation ameliorated the HFFrD-induced enhanced lipogenesis and lipid peroxidation. An anti-inflammatory effect of L-methionine was also observed through the inhibition of the release of proinflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, the hepatic SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway was associated with the beneficial effects of L-methionine. This study demonstrates that L-methionine supplementation in HFFrD-fed rats improves their liver pathology via regulation of lipogenesis, inflammation, and the SIRT1/AMPK pathway, thus encouraging its clinical evaluation for the treatment of NASH.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function HOT Articles 2022


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...