A review on selenium-enriched proteins: preparation, purification, identification, bioavailability, bioactivities and application
Abstract
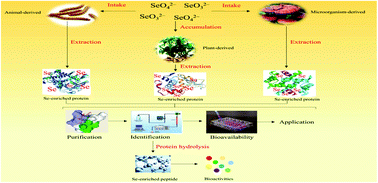
Selenium (Se) deficiency can cause many diseases and thereby affect human health. Traditional inorganic Se supplements have disadvantages of toxicity and low bioavailability. Se-Enriched proteins exhibit good bio-accessibility and high biological activities. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the preparation, purification, identification, bioavailability, bioactivities and application of Se-enriched proteins. The method of extracting Se-enriched proteins from animals, microorganisms and plants mainly includes solvent extraction (water, salt, ethanol and alkali solution extraction) and novel extraction technologies (ultrasound-assisted and pulsed electric field assisted extraction). Se-Enriched proteins and their hydrolysates exhibit good bioactivities, mainly including antioxidant activity, immune regulation, neuroprotective activity, and inhibition of hyperglycemic activity, among others. Future research should focus on the relationship between Se-enriched protein metabolism and the selenium regulatory protein metabolic pathway by using multi-omics technology. In addition, it is necessary to comprehensively study the structure–activity relationship of Se-enriched proteins/hydrolysates from different sources, to further clarify their bioactive mechanism and to verify their health benefits in vivo.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...