Impact of food processing on postprandial glycaemic and appetite responses in healthy adults: a randomized, controlled trial†‡
Abstract
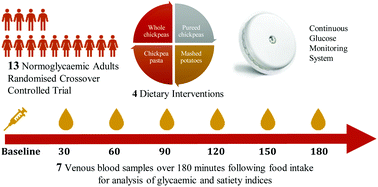
Chickpeas are among the lowest glycaemic index carbohydrate foods eliciting protracted digestion and enhanced satiety responses. In vitro studies suggest that mechanical processing of chickpeas significantly increases starch digestion. However, there is little evidence regarding the impact of processing on postprandial glycaemic response in response to chickpea intake in vivo. Therefore, the aim of this study was to determine the effect of mechanical processing on postprandial interstitial glycaemic and satiety responses in humans. In a randomised crossover design, thirteen normoglycaemic adults attended 4 separate laboratory visits following an overnight fast. On each occasion, one of four test meals, matched for available carbohydrate content and consisting of different physical forms of chickpeas (whole, puree, and pasta) or control (mashed potato), was administered followed by a subsequent standardised lunch meal. Continuous glucose monitoring captured interstitial glucose responses, accompanied by periodic venous blood samples for retrospective analysis of C-peptide, glucagon like peptide-1 (GLP-1), ghrelin, leptin, resistin, and cortisol. Subjective appetite responses were measured by Visual Analogue Scale (VAS). Postprandial glycaemic responses were comparable between chickpea treatments albeit significantly lower than the control (p < 0.001). Similarly, all chickpea treatments elicited significantly lower C-peptide and GLP-1 responses compared to the control (p < 0.05), accompanied by enhanced subjective satiety responses (p < 0.05), whilst no significant differences in satiety hormones were detected among different intervention groups (p > 0.05). Chickpea consumption elicits low postprandial glycaemic responses and enhanced subjective satiety responses irrespective of processing methods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...