Adherence to the MIND diet and the risk of cardiovascular disease in adults: a cohort study
Abstract
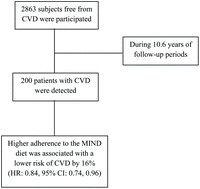
The Mediterranean-DASH intervention for neurodegenerative delay (MIND) and cardiovascular disease (CVD) has yet to be studied. As a result, the objective of this study was to investigate if there was a link between MIND diet adherence and the risk of CVD in adults over a 10.6-year period of time. There were 2863 participants in this research cohort who were free of CVD and were followed-up for 10.6 years. Using a validated food frequency questionnaire (FFQ), the MIND diet score was calculated. Reliable medical data was used to evaluate cardiovascular events, including coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, and CVD-related mortality. A total of 200 CVD occurrences (159 CHD, 21 stroke, and 20 CVD fatalities) were documented throughout the 10.6-year follow-up period. Our results indicated each increase in MIND diet score reduced the incidence of CVD by 16% (HR: 0.84; 95% CI: 0.74 to 0.96). We also detected an inverse association relationship between the MIND diet and the incidence of CVD after classifying the MIND diet score into tertiles as well (HR: 0.68; 95% CI: 0.47 to 0.97). Among the components of the MIND diet, each increase in whole grains, green leafy vegetables, and beans reduced the risk of CVD by 60%, 45%, and 65%, respectively. Finally, our findings revealed that the higher adherence to the MIND was associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular events. Besides, we found an inverse association between consumption of whole grains, green leafy vegetables, and beans and the number of CVD incidents. However, more well-designed cohort studies are needed before conclusive conclusions can be formed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...