Reinforcement learning-based real-time control of coastal urban stormwater systems to mitigate flooding and improve water quality
Abstract
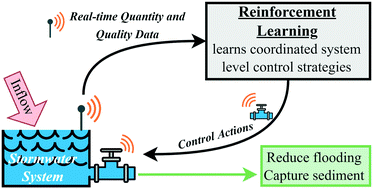
Real-time control of stormwater systems can reduce flooding and improve water quality. Current industry real-time control strategies use simple rules based on water quantity parameters at a local scale. However, system-level control methods that also incorporate observations of water quality could provide improved control and performance. Therefore, the objective of this research is to evaluate the impact of local and system-level control approaches on flooding and sediment-related water quality in a stormwater system within the flood-prone coastal city of Norfolk, Virginia, USA. Deep reinforcement learning (RL), an emerging machine learning technique, is used to learn system-level control policies that attempt to balance flood mitigation and treatment of sediment. RL is compared to the conventional stormwater system and two methods of local-scale rule-based control: (i) industry standard predictive rule-based control with a fixed detention time and (ii) rules based on water quality observations. For the studied system, both methods of rule-based control improved water quality compared to the passive system, but increased total system flooding due to uncoordinated releases of stormwater. An RL agent learned controls that maintained target pond levels while reducing total system flooding by 4% compared to the passive system. When pre-trained from the RL agent that learned to reduce flooding, another RL agent was able to learn to decrease TSS export by an average of 52% compared to the passive system and with an average of 5% less flooding than the rule-based control methods. As the complexity of stormwater RTC implementations grows and climate change continues, system-level control approaches such as the RL used here will be needed to help mitigate flooding and protect water quality.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Data-intensive water systems management and operation


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...