Metabolomic and bioenergetic responses of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells following exposure to commercial copper hydroxide nanopesticide†
Abstract
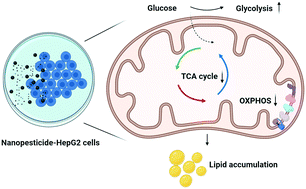
Copper hydroxide (Cu(OH)2) nanopesticide formulas are becoming more frequently used in agriculture; however, human exposure risks are not completely characterized. Here, the effect of Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide exposure on cell metabolism was assessed using metabolomics and bioenergetic assessments in the human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell line. Cell responses to the nanopesticide were also compared to that observed with conventional copper sulfate. Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide was effectively dispersed in the culture medium, preferentially taken up into cells, and showed similar effects on metabolite levels and bioenergetics of cells when compared to copper ions alone (25 μg mL−1). Both exposures increased the abundance of metabolites involved in glycolysis in response to energetic stress. In addition, both α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and isocitrate dehydrogenase were decreased in relative transcript levels and enzyme activity by the nanopesticide and copper ions. There was also an accumulation of tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle intermediates in the cells, pointing to decreased activity of the TCA cycle, which was associated with oxidative stress and impaired oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Metabolomics indicated a metabolic shift from OXPHOS to glycolysis and lipid accumulation with exposure to the Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide and copper ions. This study provides a comprehensive understanding of Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide exposure in relation to metabolic activity and mitochondrial function.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nano-bio interactions


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...