Occurrence and stability of ptesculentoside, caudatoside and ptaquiloside in surface waters†
Abstract
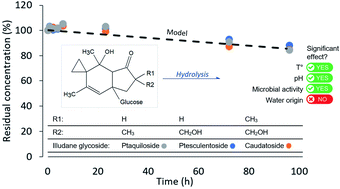
The illudane glycosides ptesculentoside (PTE), caudatoside (CAU) and ptaquiloside (PTA) are found in bracken ferns (Pteridium sp.). PTA is known to contaminate water bodies adjacent to bracken ferns and hence contribute to water toxicity. This study for the first time reports the presence of PTE and CAU in surface waters with concentrations up to 5.3 μg L−1 and outlines their stability under semi-natural conditions using water of two diverse lakes at their natural pH or pH adjusted to 6.5, with temperature controlled at 5 or 15 °C, and in the presence or absence of microbial activity. Under the same set of tested conditions the three illudane glycosides degraded at similar rates: with half-lives of approximately two days at pH 7.4 and 15 °C, and approximately 12 days at pH 5.2–6.5 and 5 °C. The water origin had significant influence on the degradation rates, but only due to its difference in pH. In most cases, the degradation rates of all the three illudane glycosides could be predicted using the existing first-order model for PTA hydrolysis. As PTE and CAU exhibit the same leaching pattern and stability as PTA, previous predictions of bracken environmental impact are likely underestimated, as PTE and CAU have not been monitored and included in the risk assessment.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Recent Open Access Articles - Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts and Contaminant remediation and fate


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...