Local reaction environment for selective electroreduction of carbon monoxide†
Abstract
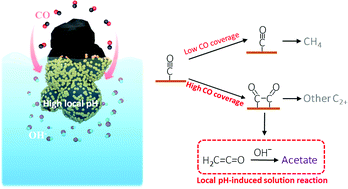
The electroreduction of CO2 to multi-carbon products (C2+) is an attractive route for high-density renewable energy storage, but catalytic selectivity toward a desired C2+ product is low. Although the pH in the vicinity of the catalysts has previously been correlated with selectivity of C2+ products, solid evidence of the local pH effect on specific C2+ products is lacking. Here, we present a very simple strategy for experimentally probing the local pH value in GDE-based high-rate CO electroreduction via the CO2 capture rate. From the local pH determination method as well as the consideration of other possibilities that may influence the C2+ formation, we explicitly demonstrate that the increased OH− concentration near the cathodic GDE surface in CO reduction can significantly facilitate acetate formation via a homogeneous solution reaction which is the key step, influenced by local pH near the cathode surface, correspondingly inhibiting other C2+ products such as ethanol, n-propanol and C2H4. Notably, a total C2+ faradaic efficiency of >90% that encompasses up to nearly 50% acetate faradaic efficiency is achieved via elevating average local OH− concentration. In addition, the exploration of the link between local CO availability and the specific C2+ selectivity demonstrates that high CO coverage is required for C2+ formation owing to a preferred CO coupling. Further analysis indicates that a certain intermediate should be directly shared for acetate and ethanol, but the relevant reaction paths of this intermediate may be separated from that of C2H4.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...