Hydrogen generation via ammonia decomposition on highly efficient and stable Ru-free catalysts: approaching complete conversion at 450 °C†
Abstract
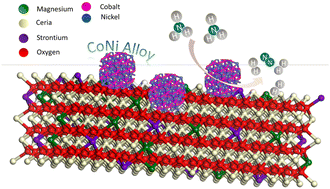
Hydrogen (H2) is a prospective zero-carbon and high-energy-density fuel alternative to fossil fuels for generating power and clean energy. Ammonia (NH3) is a promising H2 (17.7%) carrier, which can easily overcome the challenges associated with H2 storage and transportation. Thermocatalytic ammonia decomposition reaction (ADR) is an effective way to produce clean H2 but it relies on the use of expensive and rare ruthenium (Ru)-based catalysts at elevated temperatures (>500 °C), hence is not sustainable and economically feasible. Herein, we report a synergistic strategy to design a heterostructured Ru-free catalyst, consisting of CoNi alloy nanoparticles well-dispersed on a MgO–CeO2–SrO mixed oxide support with potassium promotion. The resulting K–CoNialloy–MgO–CeO2–SrO catalyst presents 97.7% and 87.5% NH3 conversion efficiency at 450 °C at gas hourly space velocities (GHSVs) of 6000 and 12 000 mL h−1 gcat−1, respectively. At 500 °C, the H2 production rate (57.75 mmol gcat−1 min−1) becomes comparable to that of most of the reported Ru-based catalysts. The catalyst stability has been successfully demonstrated in both a fixed-bed reactor under high pressure (120 h at 5.0 bar) and a membrane reactor prototype (600 h at 1.5 bar) at 500 °C. High-temperature in situ XPS analysis, temperature-programmed desorption/reduction, and density functional theory calculations have been carried out to elucidate the possible active sites and performance enhancement mechanisms. This work highlights the importance of constructing optimal interfaces between active metal nanoparticles and oxide support for boosting the NH3 to H2 conversion efficiency and long-term stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...