The surface composition of amino acid – halide salt solutions is pH-dependent†
Abstract
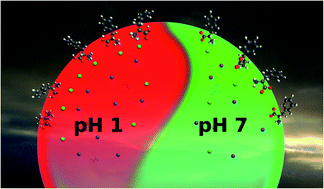
In atmospheric aerosol particles, the chemical surface composition governs both heterogenous chemical reactions with gas-phase species and the ability to act as nuclei for cloud droplets. The pH in aerosol particles is expected to affect these properties, but it is very challenging to measure the pH in individual droplets, precluding the investigation of its influence on the particle's surface composition. In this work, we use photoelectron spectroscopy to explore how the surface composition of aqueous solutions containing inorganic salt and amino acids changes as a function of pH. We observe a change by a factor of 4–5 of the relative distribution of inorganic ions at the surface of a liquid water jet, as a function of solution pH and type of amino acid in the solution. The driving forces for the surface enhancement or depletion are ion pairing and the formation of charged layers close to the aqueous surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...