Antitumor effects of new glycoconjugated PtII agents dual-targeting GLUT1 and Pgp proteins†
Abstract
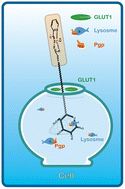
A novel and highly efficient dual-targeting PtII system was designed to improve the drug delivery capacity and selectivity in cancer treatment. The dual-targeting monofunctional PtII complexes (1–8) having glycosylated pendants as tridentated ligand were achieved by introducing glycosylation modification in the thioaminocarbazone compounds with potential lysosomal targeting ability. The structures and stability of 1–8 were further established by various techniques. Molecular docking studies showed that 2 was efficiently docked into glucose transporters protein 1 (GLUT1) and P-glycoprotein (Pgp) proteins with the optimal CDocker-interaction-energy of −64.84 and −48.85 kcal mol−1. Complex 2 with higher protein binding capacity demonstrated significant and broad-spectrum antitumor efficacy in vitro, even exhibiting a half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value (∼10 μM) than cisplatin (∼17 μM) against human lung adenocarcinoma cells (A549). The inhibitor experiment revealed GLUT-mediated uptake of 2, and the subcellular localization experiment in A549 also proved that 2 could be localized in the lysosome, thereby causing cell apoptosis. Moreover, cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA) confirmed the binding of 2 with the target proteins of GLUT1 and Pgp. The above results indicated that 2 represents a potential anticancer candidate with dual-targeting functions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...