Diosgenin derivatives developed from Pd(ii) catalysed dehydrogenative coupling exert an effect on breast cancer cells by abrogating their growth and facilitating apoptosis via regulating the AKT1 pathway†
Abstract
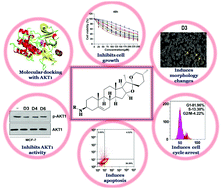
Palladium metallates containing 4-oxo-4H-chromene-3-carbaldehyde derived ONS donor Schiff bases were synthesized and their efficacy was tested in the direct amination of diosgenin – a phyto steroid. Based on the pharmacological importance of diosgenin, the obtained derivatives were exposed to study their effect on breast cancer cells where they significantly reduced the growth of cancer cells and left non-malignant breast epithelial cells unaffected. Among the derivatives, D3, D4 and D6 showed a better anti-proliferative effect and further analysis revealed that the D3, D4 and D6 derivatives markedly promoted cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by attenuation of the AKT1 signalling pathway.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...