Suppression of reversible photocyclization reaction induced fluorescence enhancement: a theoretical study†
Abstract
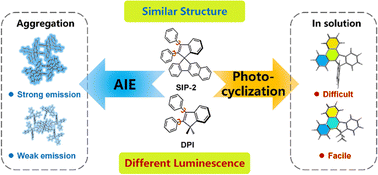
Aggregation-induced emission (AIE) materials with photocyclization (PC) reactions exhibit rich photophysical and photochemical activities. Understanding the mechanism behind is essential to the design of effective AIE materials. Herein, we employ a polarizable continuum model (PCM) and the hybrid quantum mechanics and molecular mechanics (QM/MM) approach, to study the luminescent properties of PC-typed AIEgens, SIP-2 and DPI, in both solution and crystalline states. The calculated results indicate that the fluorescence quantum yields (ΦF) of SIP-2 and DPI under different environments are mainly related to the competition between the PC reaction and aggregation induced restriction of phenyl ring rotational motions. In solution, SIP-2 and DPI undergo PC reactions to form a C–C bond between the phenyl rings A and B, which provides an important non-radiative decay channel and dramatically reduces the fluorescence intensity. Upon aggregation, the restricted rotational motion of rings A and B blocks the PC reaction and reduces the reorganization energy, which lowers the non-radiative decay rate constant (kIC) and benefits the ΦF. This is consistent with the experimental phenomenon that both SIP-2 and DPI exhibit the AIE effect. In addition, the introduction of the rigid spiro backbone of SIP-2 increases the steric effect, further limiting the phenyl ring rotation and PC reaction, resulting in an increase in the fluorescence intensity. Our calculations not only show the detailed mechanism of PC-typed AIEgens but also provide theoretical guidance for the further rational design of efficient AIEgens.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...