Electronic structure, defect properties, and optimization of the band gap of the earth-abundant and low-toxicity photovoltaic absorber Cu3SbS4
Abstract
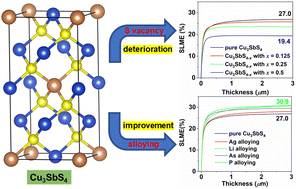
Searching for an earth-abundant and environment-friendly absorber for thin-film solar cells that provides similar power conversion efficiency to CdTe and Cu(In,Ga)Se2 is of great importance for large-scale applications. Success would change the world's solar energy supply to an even more sustainable material resource. In this paper, we have studied by first-principles calculations the electronic structure and defect properties of the promising absorber Cu3SbS4. Its electronic properties, like direct band gap, high absorption coefficient, and light carrier effective masses, satisfy the requirements for an absorber except for its somewhat too small band gap energy. Sulfur and copper vacancies are easily formed defects in Cu3SbS4, where the S vacancy shrinks the band gap and degrades the material. This probably explains the experimental findings of a rather poor device performance. The suitable preparation conditions for Cu3SbS4 as an absorber are anticipated to be Cu-poor, Sb-moderate, and S-rich conditions. Herein, isovalent element alloying is demonstrated to be an effective way to increase the gap energy and thereby improve the material properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...