In situ activation of green sorbents for CO2 capture upon end group backbiting†
Abstract
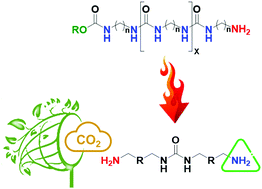
Thermolysis of a urethane end group was observed as a first time phenomenon during activation. This unzipping mechanism revealed a new amine tethering point producing a diamine-terminated oligourea ([10]-OU), acting as a green sorbent for CO2 capturing. The oligomer backbites its end group to form propylene carbonate (PC), as proved by in situ TGA-MS, which can reflect the polymer performance by maximizing its capturing capacity. Cross polarization magic angle spinning (CP-MAS) NMR spectroscopy verified the formation of the proven ionic carbamate (1:2 mechanism) with a chemical shift at 161.7 ppm due to activation desorption at higher temperatures, viz., 100 °C (in vacuo) accompanied with bicarbonate ions (1:1 mechanism) with a peak centered at 164.9 ppm. Fortunately, the amines formed from in situ thermolysis explain the abnormal behavior (carbamates versus bicarbonates) of the prepared sample. Finally, ex situ ATR-FTIR proved the decomposition of urethanes, which can be confirmed by the disappearance of the pre-assigned peak centered at 1691 cm−1. DFT calculations supported the thermolysis of the urethane end group at elevated temperatures, and provided structural insights into the formed products.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...