The thermal isomerization of benzvalyne to benzyne†
Abstract
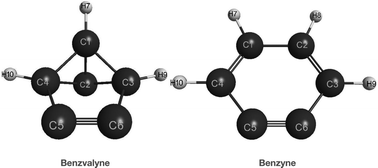
The isomerization of the highly strained benzvalyne structure to o-benzyne has been investigated using MCSCF and CCSD(T) levels of theory. Two reaction channels were modeled: the disrotatory one which leads directly to the benzyne product, and the conrotatory one which leads to an intermediate which can subsequently lead to the benzyne product. Energies at the MRMP2 level give 22.9 kcal mol−1 for the disrotatory channel and 21.7 and 1.4 kcal mol−1 for the two steps in the conrotatory one. However, the CCSD(T) energies give 19.3 and 14.2 kcal mol−1 for the two conrotatory steps. The first step of the conrotatory channel is significantly higher than the second so is rate determining for this channel. Comparison of the two separate channels shows that the conrotatory has just a slight energetic edge of 1.2 kcal mol−1 at the MRMP2 level. We did not compute the disrotatory channel at the CCSD(T) level due to the significant biradical nature of the wavefunction with natural orbital occupation numbers of 1.2 and 0.8 in the active space.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...