The effects of thermal treatment and irradiation on the chemical properties of natural diamonds†
Abstract
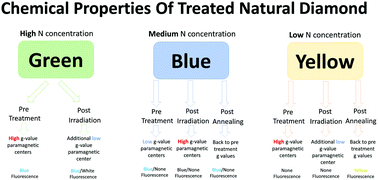
The modification of nitrogen-contaminated diamonds into color-enhanced diamonds is usually achieved by irradiation and thermal treatment (annealing). These treatments affect nitrogen contamination chemical bonding, vacancy concentration, and atom orientation centers in the diamond lattice. In this study, natural diamonds were subjected to irradiation and thermal annealing color enhancement treatments to produce green, blue, and yellow fancy diamonds. The study followed the changes that occur during treatment relying on visual assessment, fluorescence, UV-vis, FTIR, and EPR spectroscopy to characterize paramagnetic centers. The results indicated that diamonds containing high levels of nitrogen contamination presented a relatively high carbon-centered radical concentration. Two paramagnetic groups with different g-values were found, namely, low g-value centers of 2.0017–2.0027 and high g-value centers of 2.0028–2.0035. It is suggested that the 2.0017–2.0022 centers correlate with blue centers, whereas the 2.0023–2.0027 centers correlate with yellow centers. It was also found that thermal treatment was required to produce blue and yellow fancy diamonds, whereas no such treatment was needed to produce green diamonds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...