Electrostatic penetration effects stand at the heart of aromatic π interactions†
Abstract
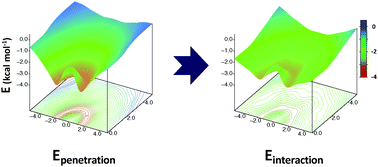
The nature of the interaction in benzene-containing dimers has been analysed by means of Symmetry Adapted Perturbation Theory (SAPT). The total interaction energy and the preference for the dimers to adopt slipped structures are, apparently, consequence of the balance between repulsion and dispersion. However, our results indicate that this only holds when trends are analysed using fixed intermolecular distances. Employing the most favourable separations between rings it turns out that the changes on the total interaction energy are mostly controlled by electrostatics, while repulsion and dispersion cancel each other to a great extent. Most of the electrostatic contribution is accounted for by electrostatic penetration, so a description based on multipoles should not be employed to rationalise the interaction in benzene-containing dimers. The changes on the interaction energy in benzene-containing dimers are steered by electrostatic penetration which, though often overlooked, plays an essential role for the description of aromatic π interactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...